OUR MODEL
Our pedagogical model is a special education method that responds to high-potential children through a teaching scheme where the student assumes an active role with their learning process and is student-centered as person.
The active learning allows students to be offered a leading role in their learning by involving them in challenging activities such as asking questions, solving problems, sharing results and learning from others in a continuous process of of knowledge construction. These activities cultivate a productive, participatory, reflective and critical attitude towards scientific and social phenomena. In this process, the teacher assumes the role of facilitator and guide who uses active teaching strategies and is supported by cutting-edge technologies.
The second element of this pedagogical model, learning centered on the student as a person, is based on the consideration that the student has the capacity to transform and improve himself and their environment through a comprehensive educational process that attends to the development of the cognitive, affective and social spheres. This comprehensive training implies that the student learns knowledge, skills, attitudes and values, while promoting the search for individual identity and the ideal of service to others as a personal life project.
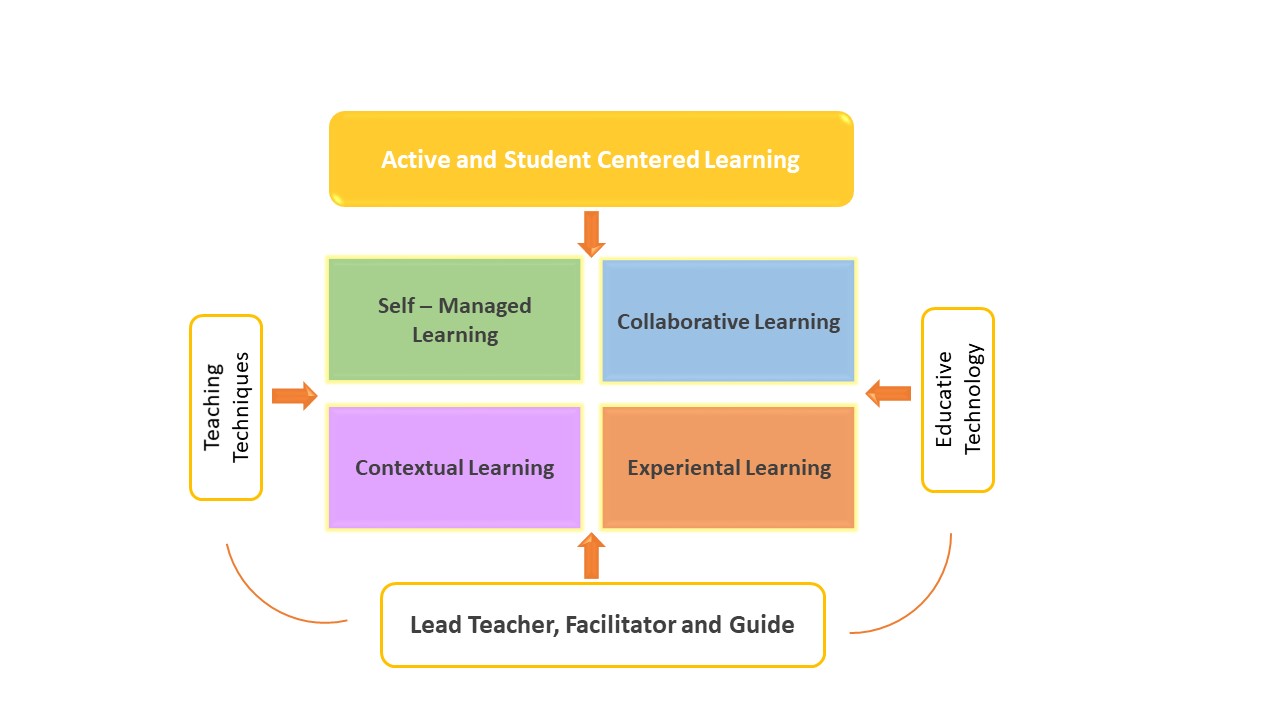

This pedagogical model is based on four forms of learning that are integrated and shape the extracurricular activities offered by the center, both at the junior high and high school levels.
SELF-MANAGED LEARNING
This learning touches the essence of the talented student, since it allows him to deploy personal initiatives, perseverance, will and effort to pursue the achievement of his learning. It implies a cyclical process in which students monitor the effectiveness of their strategies, generate motivation, self-knowledge and self-efficacy of their own actions, thus transcending academic environments and impacting learning for life (B. Zimmerman)
COLLABORATIVE LEARNING
The best experiences in programs aimed at developing talent consider that it is considerably improved by working with the peer group, where, under the direction and support of the teacher, students learn to confront their points of view, accept their differences, help each other, be supportive, work on common projects, set their own standards, fulfill collectively adopted commitments and socially build knowledge by forming true learning communities (R. Johnson, D. Johnson and L. Vygotsky).
CONTEXTUAL LEARNING
This learning consists of linking theoretical content with reality, presenting real scenarios where students have to analyze and reflect on situations from multiple perspectives, developing critical, creative, divergent and complex thinking and offering solutions with scientific arguments (D. Ausubel and J. Brunner).
EXPERIENTIAL LEARNING
This learning offers the opportunity to participate and engage in a meaningful way in activities and learning environments in which the student faces significant challenges, reflect on the results, derive knowledge from from experience and apply new knowledge to improve action (J. Dewey and D. Kolb).
